Introduction:
Insulin resistance, exercise, and obesity form a complex web of interactions that have profound effects on our overall health and well-being.
These factors are intimately connected, and understanding their relationship is crucial for preventing and managing chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
In this article, we will discuss insulin resistance, the role of exercise in combating it, and how obesity influences this intricate balance.
Insulin Resistance in Depth:
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, plays a central role in regulating blood sugar levels.
Insulin resistance occurs when our body’s cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin.
As a consequence, the pancreas compensates by producing more insulin, leading to elevated insulin levels in the bloodstream. Over time, this can progress to type 2 diabetes if not effectively managed.
Causes of Insulin Resistance:
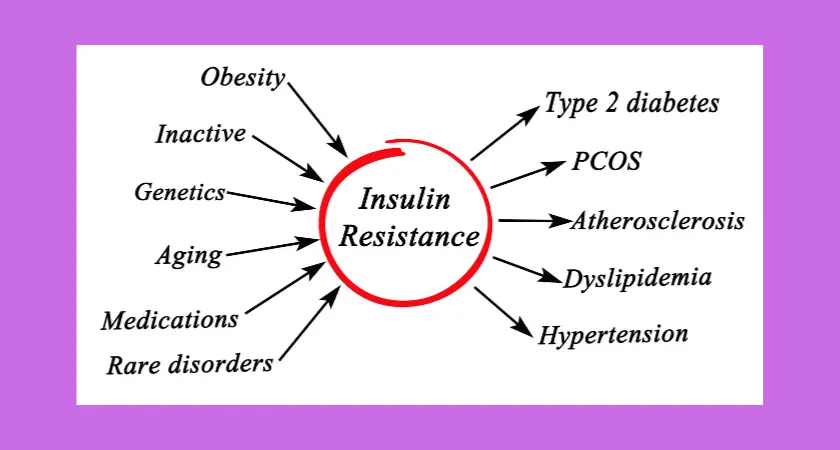
Several factors contribute to the development of insulin resistance, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions.
Excess body weight, particularly abdominal obesity, is strongly associated with insulin resistance.
Sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits (such as high intake of sugary foods and drinks), and chronic inflammation also play a role.
According to Carewell.Com, “Insulin resistance is a common medical condition, affecting up to 40% of adults”.
Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance:
In individuals with insulin resistance, the cells do not respond effectively to insulin’s signals, leading to impaired glucose uptake. Insulin normally binds to receptors on cell surfaces, triggering a cascade of events that allow glucose to enter the cells for energy production. However, in insulin-resistant individuals, this process is disrupted. The cells become less receptive to insulin, and glucose uptake is reduced. As a compensatory response, the pancreas produces more insulin, leading to elevated insulin levels in the bloodstream.
Implications for Health:
Insulin resistance has significant implications for our health and can contribute to the development of several conditions:
- Type 2 Diabetes: If left unmanaged, insulin resistance can progress to type 2 diabetes. With insulin resistance, the pancreas struggles to produce enough insulin to compensate for the reduced cell responsiveness. As a result, blood sugar levels remain elevated, leading to a diagnosis of diabetes.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Insulin resistance is a central feature of metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that include high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar levels, abnormal cholesterol levels, and excess abdominal fat. These factors increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Gain: Insulin resistance can contribute to weight gain and difficulties in losing weight. When cells are resistant to insulin’s signals, glucose remains in the bloodstream rather than being taken up by cells for energy. This can lead to increased fat storage and weight gain, creating a challenging cycle.
- Cardiovascular Health: Insulin resistance is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke. It promotes inflammation, impairs blood vessel function, and disrupts the balance of cholesterol and triglycerides in the bloodstream, all of which contribute to cardiovascular complications.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Insulin resistance is commonly observed in women with PCOS, a hormonal disorder characterized by irregular periods, excess hair growth, and ovarian cysts. Insulin resistance in PCOS can further exacerbate hormonal imbalances and contribute to fertility issues.
Managing Insulin Resistance:
While insulin resistance can be a challenging condition, there are several approaches to manage and improve insulin
sensitivity.

Understanding Exercise’s Impact:
Regular exercise is a powerful tool for improving insulin sensitivity, which counters insulin resistance. When we engage in physical activity, our muscles require more energy, supplied by glucose (sugar) present in the bloodstream. Through exercise, our muscles become more efficient at utilizing glucose, reducing the reliance on insulin. This enhanced glucose uptake lowers the demand for insulin and enhances insulin sensitivity.
- Physical Fitness: Regular exercise helps improve physical fitness by enhancing cardiovascular health, strengthening muscles, and increasing flexibility and endurance. Engaging in activities such as jogging, swimming, cycling, or dancing can boost your fitness level and overall vitality.
- Weight Management: Exercise plays a vital role in managing body weight. It helps burn calories, which is essential for weight loss and weight maintenance. Combining regular exercise with a balanced diet can help create a calorie deficit, leading to healthy and sustainable weight management.
- Cardiovascular Health: Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, running, or cycling, improve cardiovascular health. These activities increase heart rate and stimulate blood flow, enhancing the efficiency of the heart and blood vessels. Regular aerobic exercise reduces the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke.
- Muscle Strength and Bone Health: Resistance training, which involves activities like weightlifting or using resistance bands, strengthens muscles and promotes bone health. It helps build and maintain muscle mass, which is essential for overall strength and functionality. Resistance training also helps prevent age-related muscle loss and decreases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Mental Well-being: Exercise is not only beneficial for physical health, but also has a positive impact on mental well-being. It helps reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, boosts mood, and improves overall mental clarity. Physical activity stimulates the release of endorphins, often referred to as “feel-good” hormones, which contribute to a sense of well-being.
- Energy Levels: Regular exercise can increase energy levels and combat fatigue. Engaging in physical activity boosts circulation, improves oxygen flow, and enhances the efficiency of various body systems. As a result, you may experience increased energy and improved productivity throughout the day.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise plays a crucial role in improving insulin sensitivity, which is vital for managing insulin resistance and preventing type 2 diabetes. Physical activity helps our muscles utilize glucose more efficiently, reducing the demand for insulin. Regular exercise can lower blood sugar levels and improve overall insulin sensitivity.
- Quality Sleep: Exercise can promote better sleep quality. Engaging in physical activity helps regulate sleep patterns, increases the duration of deep sleep, and reduces sleep disturbances. However, it’s important to avoid intense exercise close to bedtime, as it may have an energizing effect and interfere with sleep.
The Influence of Obesity:
Obesity serves as a significant risk factor for insulin resistance.
Excessive body fat, particularly in the abdominal region, can contribute to chronic inflammation and the release of substances that impair insulin signaling.
Adipose tissue (fat cells) releases hormones and fatty acids that interfere with insulin’s action, further exacerbating insulin resistance.

A Vicious Cycle:
Insulin resistance and obesity often create a vicious cycle that perpetuates their negative effects.
Insulin resistance can promote weight gain by altering the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates, making it easier to accumulate body fat.
As obesity increases, the excess adipose tissue releases pro-inflammatory substances that intensify insulin resistance, setting the stage for a dangerous feedback loop.
Breaking this cycle is vital for preventing or managing conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle Changes for Improved Insulin Sensitivity:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in a combination of aerobic exercises and resistance training to enhance insulin sensitivity and manage weight effectively.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, emphasizing fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit intake of sugary beverages, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats.
- Healthy Weight Management: If overweight, even modest weight loss can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of complications.
- Sufficient Sleep: Inadequate sleep duration and poor sleep quality have been linked to insulin resistance. Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can contribute to insulin resistance. Incorporate stress-management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or engaging in hobbies to promote relaxation.
Conclusion:
Insulin resistance, exercise, and obesity are intimately intertwined factors that significantly impact our health.
By understanding their complex interplay and making proactive lifestyle changes.
These include regular exercise, adopting a balanced diet, managing weight effectively, prioritizing sufficient sleep, and reducing stress levels, we can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Empower yourself to take charge of your health today, breaking the cycle of insulin resistance and obesity for a healthier future.


