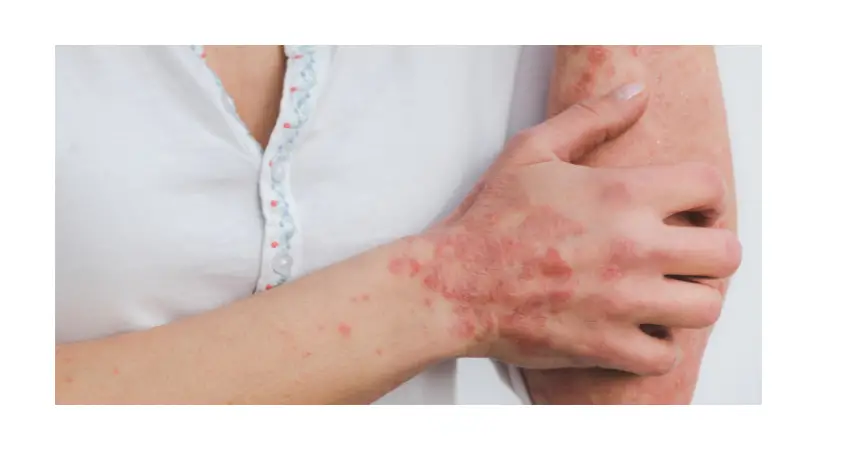
The Prevalence of Psoriasis and High Blood Pressure
Psoriasis and high blood pressure are two prevalent medical conditions that affect a significant portion of the population. According to the World Health Organization, psoriasis affects approximately 2-3% of the global population, while high blood pressure is a common condition that affects about 1.13 billion people worldwide.
While they are distinct conditions, recent research has shed light on a potential link between the two. This article aims to explore the connection between psoriasis and high blood pressure, provide insights into the management of both conditions, and highlight the importance of a holistic approach to overall well-being.
Understanding Psoriasis
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects the skin, leading to the rapid buildup of skin cells. This process results in the formation of thick, scaly patches on the skin’s surface, which can be red, itchy, and painful. Psoriasis is not contagious and can range from mild to severe.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis can vary from person to person but commonly include:
- Red patches of skin with silvery scales
- Itching, burning, or soreness
- Dry and cracked skin
- Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails
- Swollen and stiff joints
Psoriasis can affect any part of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, and genitals. In some cases, psoriasis can also affect the nails, leading to changes in their appearance.
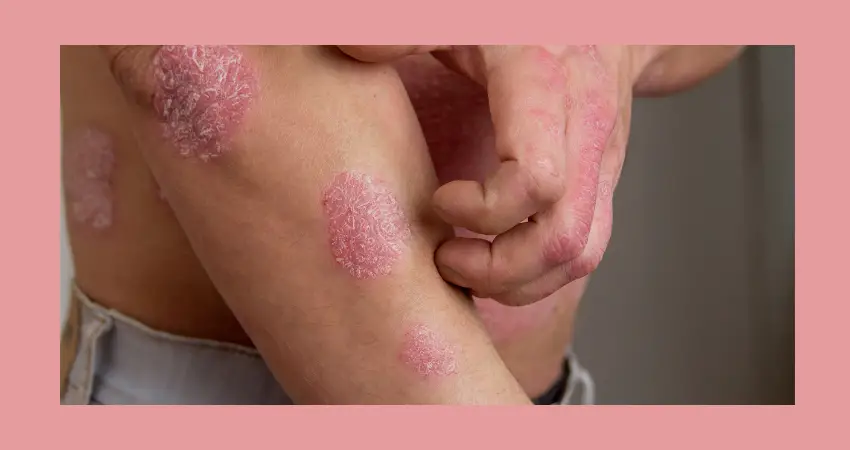
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is still unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The immune system plays a crucial role in the development of psoriasis, as it mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering an inflammatory response. This immune system dysfunction causes the rapid turnover of skin cells, leading to the characteristic symptoms of psoriasis.
Risk Factors for Psoriasis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing psoriasis, including:
- Family history of psoriasis: Having a close relative with psoriasis increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Certain infections: Infections, such as strep throat, can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms in some individuals.
- Stress: Stressful events or chronic stress can contribute to the development or exacerbation of psoriasis.
- Smoking: Smoking can worsen psoriasis symptoms and contribute to its development.
- Obesity: Excess weight or obesity is a risk factor for psoriasis, and it can also make existing symptoms more severe.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as lithium, antimalarial drugs, and beta-blockers, can trigger or aggravate psoriasis symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Understanding High Blood Pressure
What is High Blood Pressure?
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels consistently above the normal range. Blood pressure is measured using two values: systolic pressure (the top number) and diastolic pressure (the bottom number). Normal blood pressure is typically around 120/80 mmHg. When blood pressure consistently exceeds 130/80 mmHg, it is considered high.
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it typically does not cause noticeable symptoms. However, some individuals may experience symptoms such as:
- Headaches
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
- Blurred vision
These symptoms may occur in severe cases or during hypertensive crises, which require immediate medical attention.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
There are two types of high blood pressure: primary (essential) and secondary. Primary high blood pressure develops over time without any identifiable cause, while secondary high blood pressure is usually caused by an underlying health condition.
Primary high blood pressure is thought to be influenced by several factors, including:
- Genetics: Family history of high blood pressure increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Age: The risk of high blood pressure increases with age.
- Lifestyle factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and tobacco use, can contribute to the development of high blood pressure.
Secondary high blood pressure can be caused by various underlying health conditions and factors, such as:
- Kidney problems
- Hormonal disorders
- Certain medications
- Sleep apnea
- Thyroid disorders
Risk Factors for High Blood Pressure
Several factors can increase the risk of developing high blood pressure, including:
- Family history of high blood pressure: Having a close relative with high blood pressure increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Age: The risk of high blood pressure increases with age.
- Excess weight or obesity: Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of high blood pressure.
- Lack of physical activity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle is associated with higher blood pressure levels.
- Unhealthy diet: A diet high in sodium, saturated fats, and cholesterol and low in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can contribute to the development of high blood pressure.
- Chronic conditions: Certain chronic conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and sleep apnea, can increase the risk of high blood pressure.
The Connection between Psoriasis and High Blood Pressure
Research Findings
Recent studies have indicated a potential association between psoriasis and high blood pressure. Research suggests that individuals with psoriasis may have a higher risk of developing high blood pressure compared to those without the condition. A meta-analysis published in JAMA Dermatology in 2018 analyzed data from 59 studies and found that psoriasis was associated with an increased risk of hypertension. The exact mechanisms underlying this association are still being investigated.
Shared Inflammatory Pathways
Both psoriasis and high blood pressure involve chronic inflammation within the body. In psoriasis, the immune system triggers inflammation in the skin, leading to the characteristic symptoms. In high blood pressure, inflammation affects the blood vessels, causing them to narrow and stiffen, leading to increased pressure. The shared inflammatory pathways suggest a potential link between these two conditions.
The Role of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation, a common factor in both conditions, may contribute to their co-occurrence. The systemic inflammation seen in psoriasis can potentially affect blood vessel function and increase the risk of developing high blood pressure. Similarly, high blood pressure-related inflammation may exacerbate psoriasis symptoms. However, more research is needed to fully understand the complex relationship between these conditions.
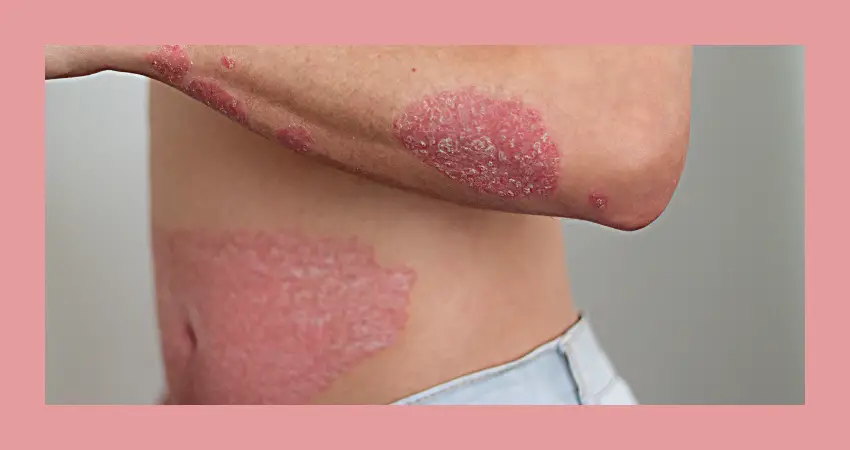
Managing Psoriasis and High Blood Pressure Simultaneously
While psoriasis and high blood pressure may present unique challenges individually, it is possible to manage both conditions effectively. Here are some strategies that can help:
Lifestyle Changes
Implementing positive lifestyle changes can have a significant impact on both psoriasis and high blood pressure. This includes:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Losing weight if overweight or obese can help improve psoriasis symptoms and reduce high blood pressure.
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can worsen psoriasis symptoms and contribute to high blood pressure. Quitting smoking is beneficial for overall health.
- Limiting alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can trigger or worsen psoriasis symptoms and contribute to high blood pressure. Moderation is key.
- Reducing stress levels: Stress can exacerbate both psoriasis and high blood pressure. Engaging in stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
- Getting sufficient sleep: Quality sleep is important for overall health. Aim for 7-8 hours of restful sleep each night.
Medication Management
Working closely with healthcare professionals is essential for managing both psoriasis and high blood pressure. They may prescribe medications tailored to each individual’s needs, such as topical treatments for psoriasis and antihypertensive drugs for high blood pressure. It is crucial to follow the prescribed treatment plan, take medications as directed, and attend regular check-ups to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan if necessary.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress can worsen both psoriasis and high blood pressure. Engaging in stress reduction techniques can help alleviate symptoms and promote overall well-being. This can include activities such as:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Practicing mindfulness
- Engaging in hobbies or activities that bring joy and relaxation
Regular Exercise
Physical activity is beneficial for both psoriasis and high blood pressure. Engaging in regular exercise helps reduce inflammation, control weight, and improve cardiovascular health. However, it is important to choose activities that are suitable for individuals with psoriasis and high blood pressure, considering any limitations or joint pain. Consult with healthcare professionals to determine the appropriate exercise regimen.
Healthy Diet Choices
Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet can support the management of both conditions. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low in sodium and saturated fats is recommended. It is also advised to limit processed foods and sugary beverages. Following a healthy diet can help control inflammation, manage weight, and promote overall heart health.
Regular Check-ups and Monitoring
Regular medical check-ups and monitoring of both psoriasis and high blood pressure are crucial. These evaluations help track progress, identify any changes or complications, and adjust the treatment plan accordingly. Regular visits to dermatologists and cardiologists, as well as periodic blood pressure measurements, can provide valuable insights into the management of both conditions.
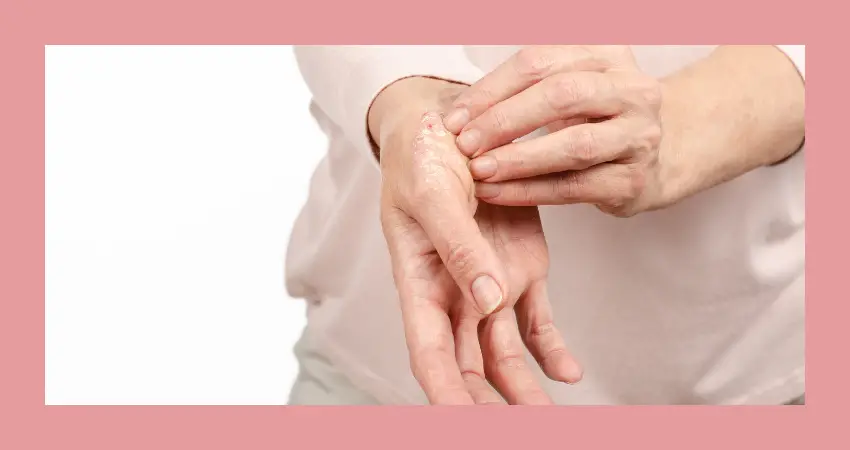
The Importance of a Holistic Approach
Managing psoriasis and high blood pressure requires a holistic approach that encompasses physical, mental, and emotional well-being. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses all aspects of these conditions.
Working with Healthcare Professionals
Collaborating with dermatologists, cardiologists, and other healthcare providers is crucial for comprehensive care. They can provide specialized guidance and develop an integrated approach tailored to individual needs. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare professionals are essential for effective management.
Support and Education
Seeking support from patient advocacy groups, online communities, or support networks can provide valuable information and emotional support. Education about the conditions can empower individuals to actively participate in their own care and make informed decisions. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can also be beneficial.
Mental and Emotional Well-being
Living with psoriasis and high blood pressure can be emotionally challenging. It is important to prioritize mental and emotional well-being. Engaging in stress reduction techniques, seeking counseling if needed, and maintaining a positive outlook can significantly impact overall well-being. Building a strong support system and fostering healthy coping mechanisms are important aspects of managing these conditions.
Conclusion
Psoriasis and high blood pressure are two prevalent conditions that may be interconnected. Understanding the link between the two and implementing appropriate management strategies is crucial for individuals with both conditions. By adopting a holistic approach that includes lifestyle changes, medication management, stress reduction techniques, regular exercise, and a healthy diet, individuals can effectively manage both psoriasis and high blood pressure, improving their overall quality of life.
FAQs
1. Can psoriasis cause high blood pressure?
Psoriasis itself does not directly cause high blood pressure. However, research suggests that individuals with psoriasis may have a higher risk of developing high blood pressure compared to those without the condition. The underlying mechanisms for this association are still being investigated.
2. Is high blood pressure more common in individuals with psoriasis?
Studies have indicated a potential association between psoriasis and high blood pressure. While more research is needed to establish a definitive link, individuals with psoriasis should be mindful of their blood pressure levels and maintain regular check-ups with healthcare professionals.
3. Can treating psoriasis improve high blood pressure?
Managing psoriasis effectively through medication, lifestyle changes, and stress reduction techniques may have a positive impact on overall health, including blood pressure management. However, individual responses may vary, and it is important to work with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance.
4. Are there any specific medications that worsen both psoriasis and high blood pressure?
Certain medications, such as beta-blockers used to treat high blood pressure, may exacerbate psoriasis symptoms in some individuals. It is essential to discuss any concerns or potential medication interactions with healthcare professionals.
5. How can stress management help in managing both conditions?
Stress can worsen symptoms of psoriasis and contribute to high blood pressure. Implementing stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or engaging in enjoyable activities, can help reduce stress levels, benefiting both conditions.