Sometimes toxic encephalopathy is difficult for healthcare providers to diagnose . Especially when the patient presents unresponsive and there is no one there to give a detailed history of the person. Alcohol encephalopathy is a very serious health problem.
Normally, these people come into the emergency room via 911. Often times they are found unresponsive or family members have noticed that they have had a change in mental status.
What is Toxic Encephalopathy?
Toxic encephalopathy is a term used to indicate when the brain is not working right because of a toxic agent. The clinical symptoms of toxic encephalopathy depend on what part of the brain cells and regions are affected.
What is Alcohol Toxic Encephalopathy?
In this article, we will talk about how excessive alcohol can cause neurotoxicity. Alcohol is one of the most commonly abused substances in the world. Alcohol dependence is the third leading cause of disease and death according to the World Health Organization.
Alcohol affects people in many different ways. This effect is very determined by genetic factors.
MRI and CAT Scan Findings of People Who Use Excessive Alcohol
When these people become sick, the liver and brain are usually impaired. Chronic alcohol use causes decreased neurotrophic factors, which leads to decreased brain functions.
Excess alcohol causes changes in the cells of the frontal cortex. This causes a loss of brain matter. This is what happens when someone is diagnosed with an alcohol syndrome.
In fact, when babies are born to mothers who abuse alcohol, the babies have diffuse brain atrophy.
On the Cat scan and the MRI, there is atrophy of the cerebellum. In chronic alcoholism, the frontal white matter of the brain is involved leading to prominent changes in the sulci.
Wernicke Encephalopathy
Wernicke encephalopathy is a neurological disorder caused by a lack of thiamine. Alcohol depletes thiamine from the body. Inadequate levels of thiamine come from an inadequate diet, decreased absorption of thiamine, and decreased levels of thiamine in the cells.
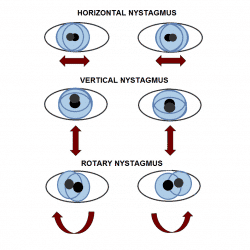
The main symptoms of Wernicke Encephalopathy are:
- Nystagmus: An involuntary movement of the eyes
- Conjugate gaze palsies: The inability to move both eyes in a vertical or horizontal manner
- Ophthalmoplegia: Paralysis or weakness of the eye muscles
How Do These Patients Present to the Emergency Department?
These patients are usually very sick when they present to the hospital.
These people gradually get sick and their loved ones will eventually call 911 because they are less responsive or unresponsive.
When they arrive at the emergency department, the health care providers will order many tests and diagnostic tests.
What Tests Will Be Ordered?
Some lab tests that will be ordered are complete blood count, chemistry, liver functions, kidney functions, and blood clotting factors.
- Complete Blood Count: The complete blood count is done because the doctors are looking for any type of blood loss or infection.
- Chemistry : The blood chemistry will show the kidney function, the liver function, and the electrolytes.
- Coagulation studies: These are extremely important studies because this test determines how fast or slow your blood will clot. The liver controls blood clotting factors. Therefor, if you have liver disease, your clotting factors may be impaired.
- Drug Toxicity: If someone comes into the emergency department unresponsive, the doctors will do a drug test to see if they have ingested any drugs,
- Cat Scan or MRI: The first diagnostic test that the emergency department will order is a MRI or Cat Scan. This is important because the doctors want to be sure the person has not had a stroke.
- Ammonia level: It is important to assess the ammonia level of a patient because with liver disease, the person cannot clear ammonia. When ammonia builds up, the person will be confused and lethargic.
What is Alcoholic Encephalopathy?
Alcohol Toxic Encephalopathy Signs and Symptoms
- High heart rate
- Sweating
- Fever
- Mental impairment
- Limb tremors
- Dizziness
- Ataxia
- Seizures
- Headache
- Dementia
- Cirrhosis
Clinical Problems Associated With Alcohol Encephalopathy
Elevated Ammonia
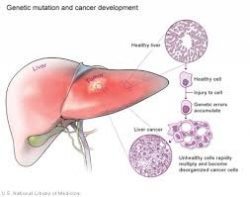
The main organ alcohol effects are the liver. This is because alcohol is metabolized in the liver. When a person has chronic alcohol abuse, the cells of the liver become impaired.
When the liver is impaired, a whole cascade of problems can occur. For example, ammonia ism often elevated in these patients. This is because ammonia is produced in the gastric tract. Ammonia is carried by the portal circulation to the liver.
When the liver is impaired, the liver is unable to convert ammonia into urea. Ammonia is highly neurotoxic.
The treatment for elevated ammonia is lactulose. Lactulose works by decreasing the amount if ammonia in the blood. The ammonia then leaves the body in the stool.
Gastric Bleed
A person who abuses alcohol is at a high risk for a GI bleed because the person has impaired clotting factors because of the liver impairment.
A person is also at risk for bleeding because if esophageal varices. Esophageal varices are enlarged blood vessels in the esophagus. They are enlarged because there is an obstruction to the portal vein. The most common cause of esophageal varices is alcohol abuse.
These clotting factors are extremely dangerous because a person can literally bleed to death if the situation is not controlled quickly. If esophageal varices start to bleed it is an emergency. The person will most likely have to have an EGD and the varices may have to be cauterized.
The person will also have to have a blood transfusion including fresh frozen plasma and sometimes platelets.
Jaundice in Liver Disease
A damaged liver can’t remove the residue of old red blood cells (bilirubin) from your blood. Bilirubin builds up and is deposited in your skin and the whites of your eyes, causing a yellow color. This is called jaundice.
Key Points for Alcoholic Liver Disease
- People who have alcoholic liver disease must stop drinking alcohol immediately.
- Alcoholic liver disease has a very high mortality and morbidity rate.
- Alcohol related liver disease is a severe form of liver disease.
Treatments for Alcohol Liver Disease
The first treatment is to stop the alcohol use. There are certain medications such as prednisone that can be used to treat the inflammation.
Lifestyle Changes
Transplant
According to the New England Journal of Medicine, A 6-month abstinence from alcohol is usually required before patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis are considered for liver transplantation. Patients whose hepatitis is not responding to medical therapy have a 6-month survival rate of approximately 30%. Since most alcoholic hepatitis deaths occur within 2 months, early liver transplantation sounds reasonable, but controversial.
Facts About Alcohol Liver Disease
- What are some hepatic disease symptoms?
- Pain in the abdomen
- Nausea and vomiting
- Jaundice
- Bilateral leg swelling
- Clubbed fingernails
- Vomited blood
- Bruising easily
Bottom Line
The liver can regenerate if it is not too damaged, and the insults to the liver are stopped. People with liver disease have been able to live a good quality life when they make lifestyle changes.
References:
https://www.nejm.org/search?q=alcohol+liver+disease&asug=
My name is Phyllis Robinson MSN, RN. I have been a Registered Nurse for 27 years in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. I am passionate about cardiac care and heart disease. I also want this blog to be an educational tool that people can refer to for traditional and alternative treatment. I will blog on heart disorders such as high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and high cholesterol.
I received my Nursing degree from Baltimore Community College.
I went on to receive my Masters in Nursing from Walden University
I have worked for almost 30 years in Critical Care with a focus on heart health. I am an advocate of preventive healthcare.